Torque Specification with Angle of Rotation
Explanation
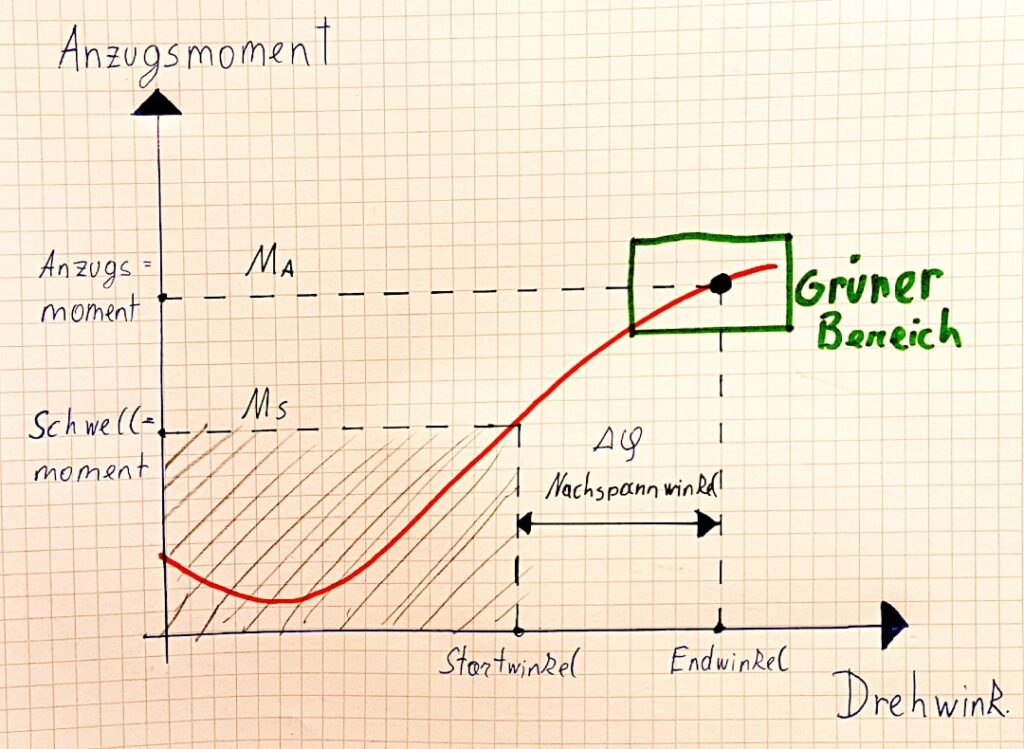
In the automotive industry and in engine construction, you will often hear the specification torque [Nm] and angle of rotation [°] for screw connections. For a screw connection with a torque and angle specification (e.g. 100 Nm + 90°), the screw is first tightened to 100 Nm using a torque wrench and then turned a further 90° (quarter turn).
The 100 Newton meters represent the initial torque, which you then increase with the angle of rotation of 90° in this example.
1) Why Torque and Angle of Rotation?
The angle of rotation specification is relevant because the required preload force can be achieved much more precisely with its help. In the angle tightening method, the yield strength of the bolt is exceeded. For this reason, this method is often used for safety-critical bolted joints. It is also an additional monitoring parameter that allows you to better inspect the bolted connections.
The specification of the angle of rotation in connection with the torque is also called the angle of further rotation. The bolt is tightened to a specified torque and then turned further by the specified angle. One advantage of this method is that retightening the bolt is no longer necessary.
2) Torque Table with Angle of Rotation
The following table provides the required torques with angle of rotation specifications for bolts from M12 to M36. These values can be applied if no additional specifications for the required bolted connection are provided. Specifications according to DIN 18800-7: 2008-11 "Combined Method".
| Dimensions | M12 | M16 | M20 | M22 | M24 | M27 | M30 | M36 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preload force F = 0.7 x fub x As [kN] | 59 | 110 | 172 | 212 | 247 | 321 | 393 | 572 |
| Pre-tightening torque Ma [Nm] | 75 | 190 | 340 | 490 | 600 | 940 | 1240 | 2100 |
| Total thickness "t" of the parts to be joined (including all lining plates and disks) d = screw diameter | Further rotation angle | Further rotation dimension | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | t < 2d | 60 | 1/6 |
| 2 | 2d = 6d | 90 | 1/4 |
| 3 | 6d =10d | 120 | 1/3 |
3) Example: Tighten the Collar Screw of the Drive Shaft
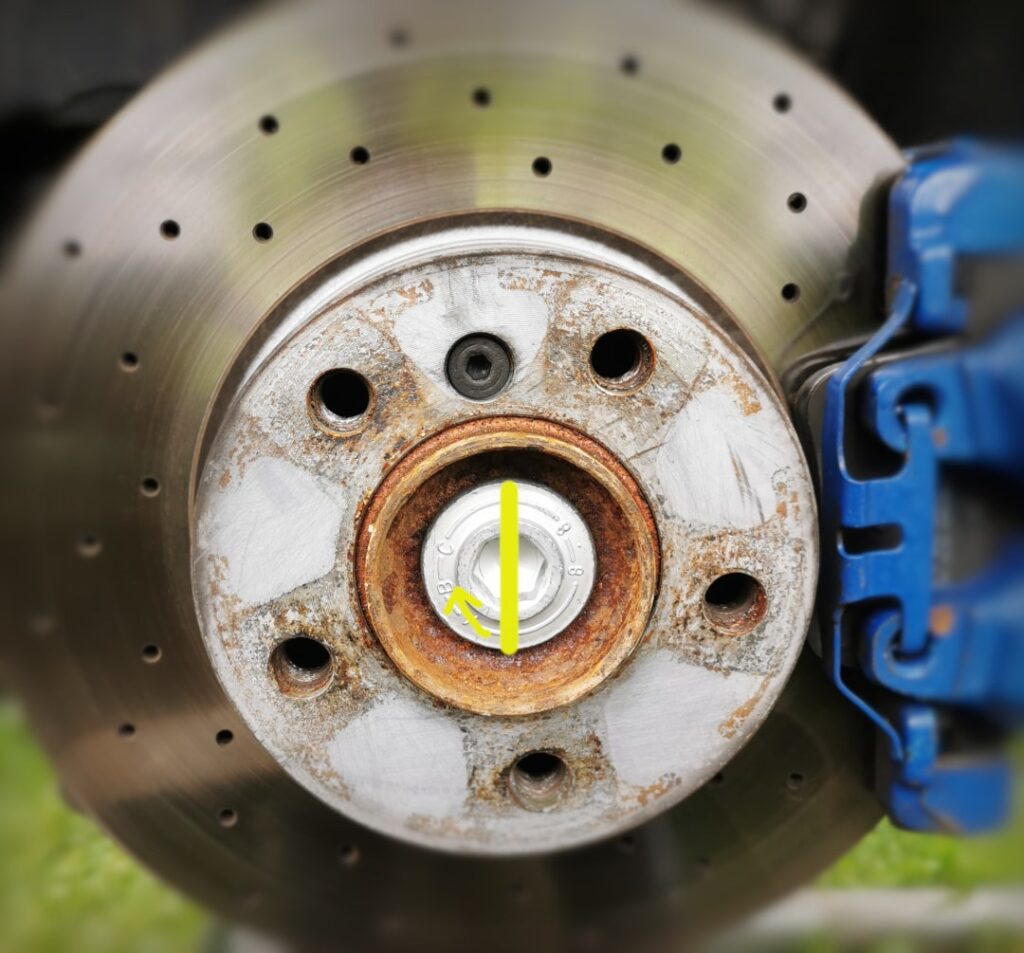
In this example, we take the flange bolt of the drive shaft from a BMW F30. This bolt should be tightened to 210 Nm + 90°.
- 【Auto Torque Wrench Set】The torque wrench set includes 1/2...
- 【High accuracy ±3%】The torque wrench with formal calibration certificate according to ISO 6789,...
- 【Safe & Easy to install】Pull the locking ring down with the to lock it in place.
When replacing the tension strut on a BMW all-wheel drive, the collar bolt of the drive shaft must be loosened. After the repair, a new collar bolt is required and this should be tightened to 210 Nm and 90°.
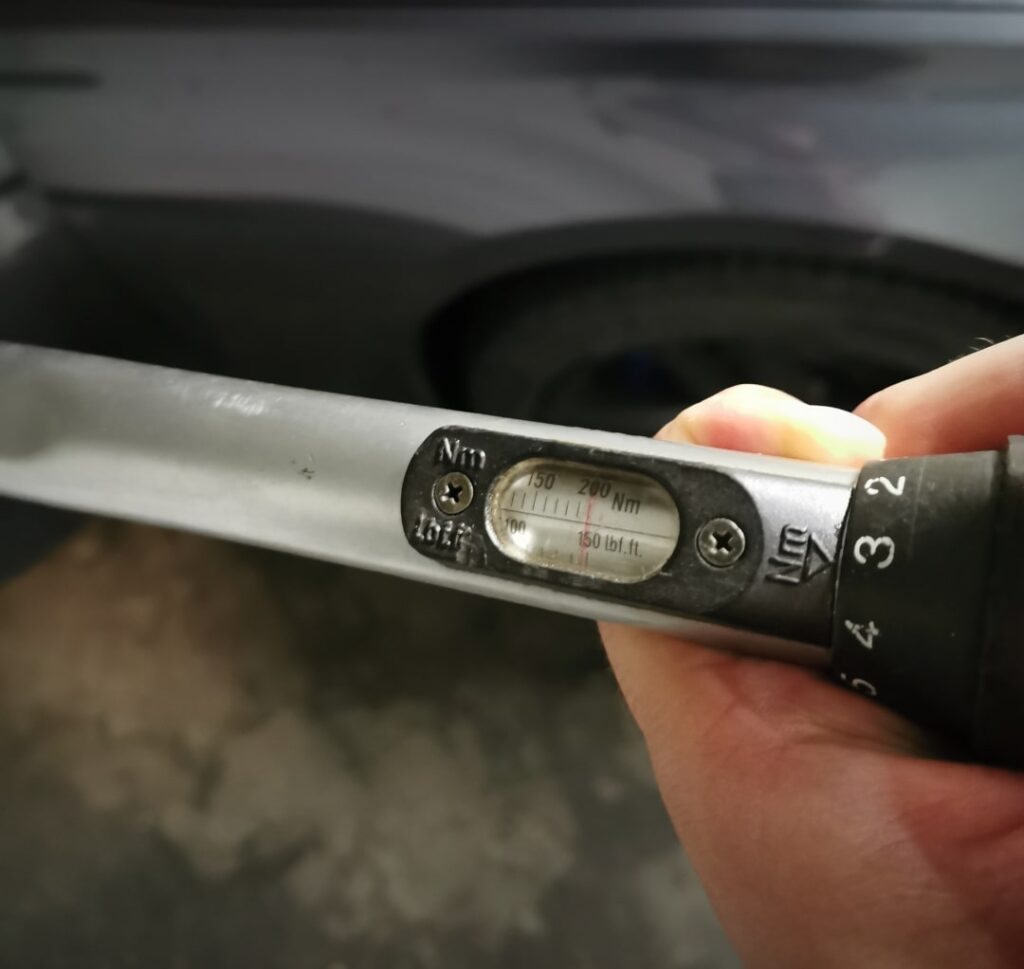
First, tighten the bolt to the required torque [Nm]. In this case, set your torque wrench to 210 Nm. If your torque wrench does not go that high, the maximum available setting will suffice.
Next, use the longest ratchet you have to turn the bolt 90° (a quarter turn) further. Mark the bolt beforehand to better track the quarter turn.
If you need more force, you can lengthen the ratchet to apply more force (leverage).
More Articles
Radlager selber wechseln – ANLEITUNG für VW Passat B7
Radlager selber wechselnAnleitung für VW Passat B7 In diesem Beitrag zeigen wir dir, wie du das vordere Radlager an einem…
Defektes Radlager – Symptome, Ursachen & die Kosten!
Defektes RadlagerSymptome, Ursachen & Kosten! Ein defektes Radlager lässt sich meistens durch knirschende oder schleifende Geräusche bemerkbar machen und ist…
URVOLAX Android 13 Autoradio – Einbau & Test im GOLF 5
URVOLAX Android 13 AutoradioEinbau & Test im GOLF 5 Ein Android Radio, welches moderne und zugleich klassische Eigenschaften besitzt? Fehlt…