EGR Valve Function & Build
Explaining how it works
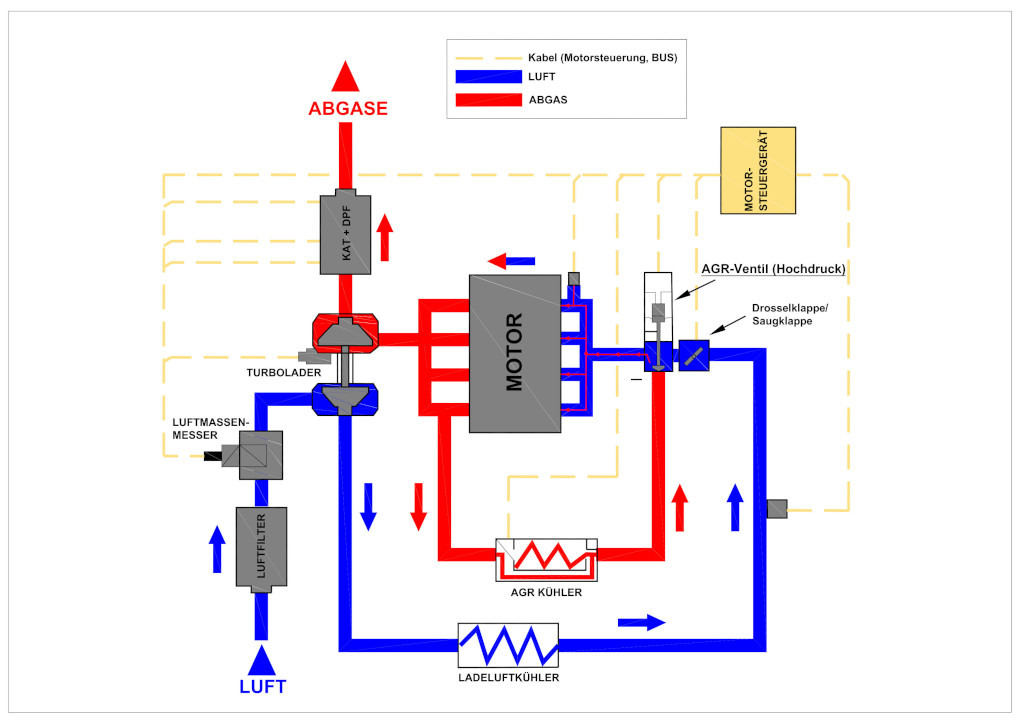
The exhaust gas recirculation valve, or EGR valve for short, is an environmentally friendly function for reducing pollutants in vehicles. In principle, exhaust gases are removed from the combustion chamber immediately after the cylinders and mixed back into the intake air in certain situations. The EGR valve and the control system behind it regulate when and how much exhaust gas is allowed to pass through.
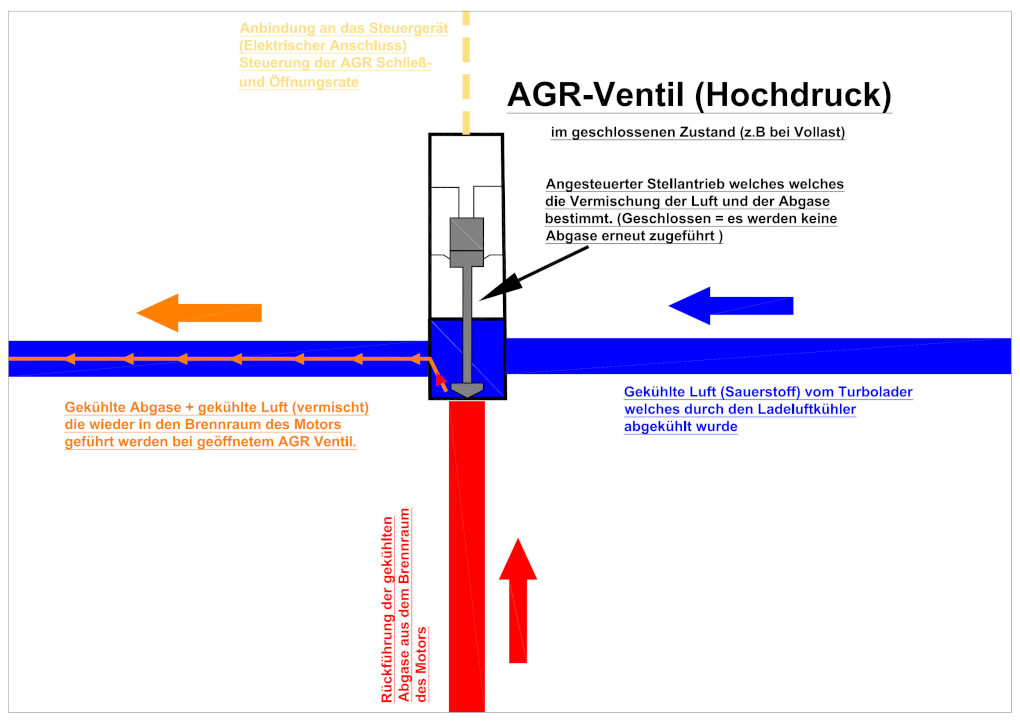
1) High-pressure EGR valve (HP EGR)
To meet the Euro 5 emissions standard for passenger cars, the high-pressure EGR valve was developed and integrated into the air intake system.
Exhaust gases from the combustion chamber are mixed with the cooled intake air from the turbocharger. The dosing is controlled by the high-pressure EGR valve.
Through this technique, less oxygen enters the cylinders. Less oxygen causes a lower combustion temperature, which reduces nitrogen oxide emissions by up to 70%. The higher the temperature, the more harmful nitrogen oxides are produced.
EGR valves are available in different versions and designs:
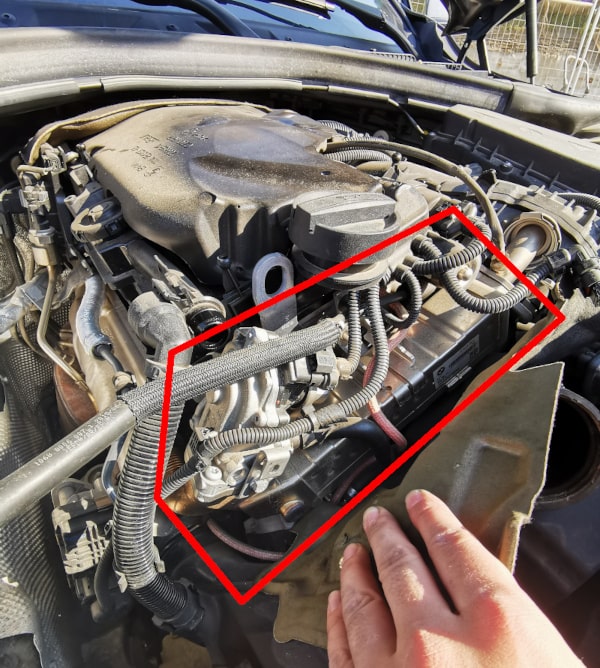

In diesel vehicles, control flaps are used to create the high pressure differential between the exhaust gases and the intake side. The mass air flow sensor monitors the regulation between the air mass and exhaust gases to indirectly calculate the recirculation rate.
2) The EGR cooler
Since simple exhaust gas recirculation is no longer sufficient to meet the latest exhaust gas standards, EGR coolers are used. Cooled exhaust gas lowers the combustion temperature even further.
This results in significantly fewer nitrogen oxides.
EGR coolers, like all components in the EGR system, are exposed to the conditions of exhaust gas condensation and temperature. Therefore, the coolers must be made from corrosion-resistant materials.
Many coolers today are equipped with a bypass valve. This is used to prevent the hot exhaust gases from cooling down during the warm-up phase.
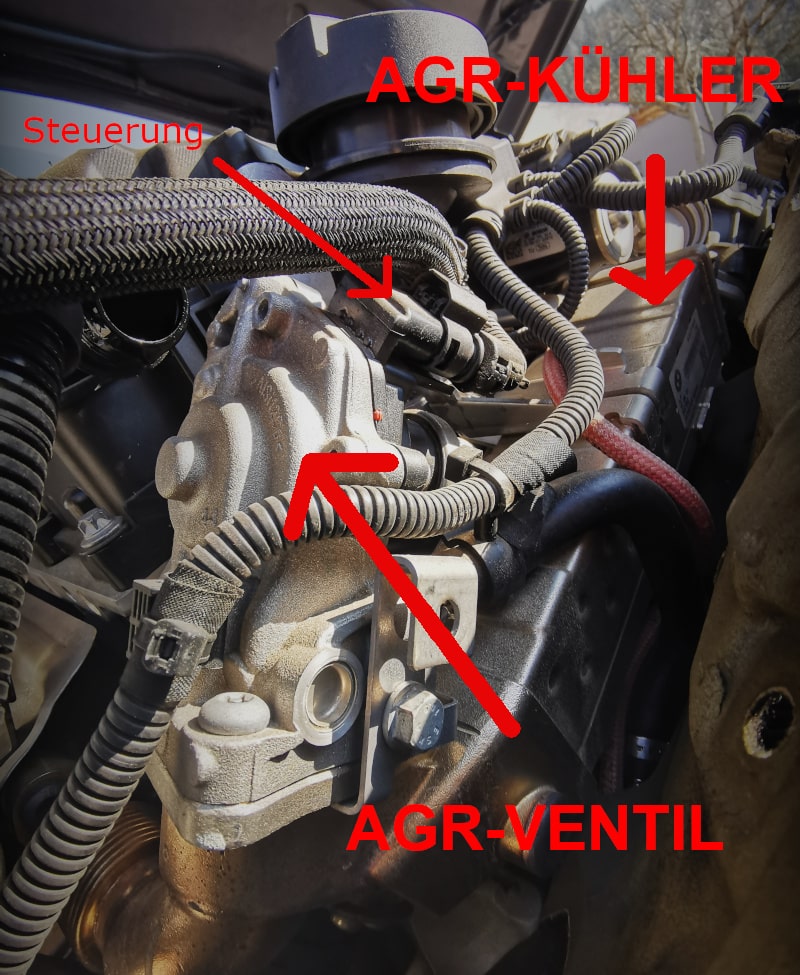
3) Cost of EGR valve & EGR cooler
The high-quality workmanship of the EGR cooler leads to a hefty price. An EGR cooler for a mid-range car can cost up to 750€. In contrast to the cooler, the EGR valve itself costs only between 50€ – 200€.
The EGR valve and the cooler are usually bolted together. If only one of these components is defective, the entire assembly usually needs to be replaced. Over time, the cooler and valve can "fuse" together and can be difficult to separate. To prevent permanent damage, we recommend replacing both the valve and the cooler.
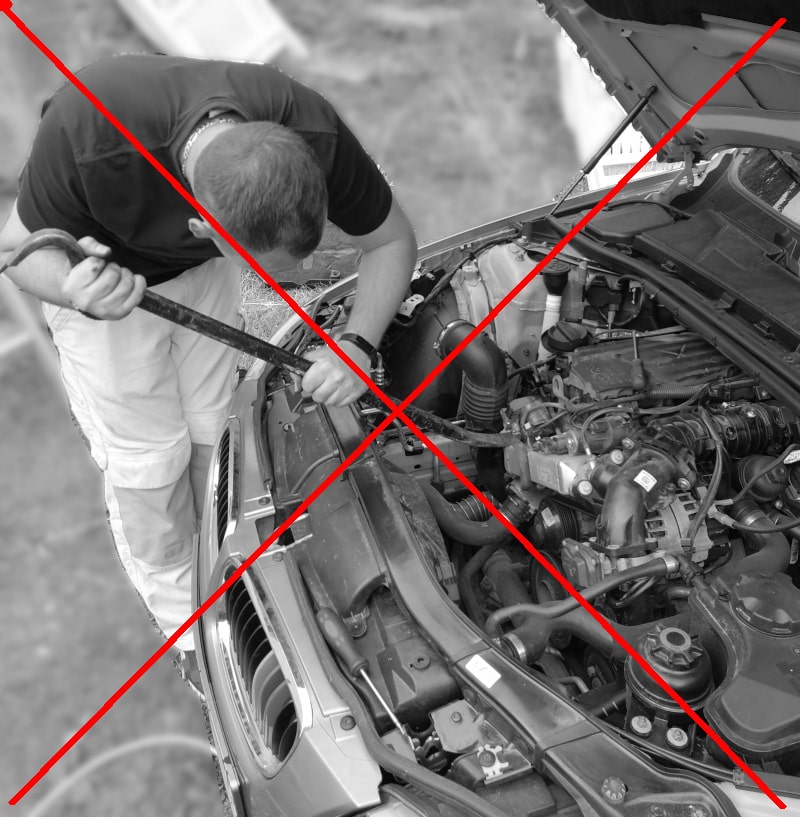

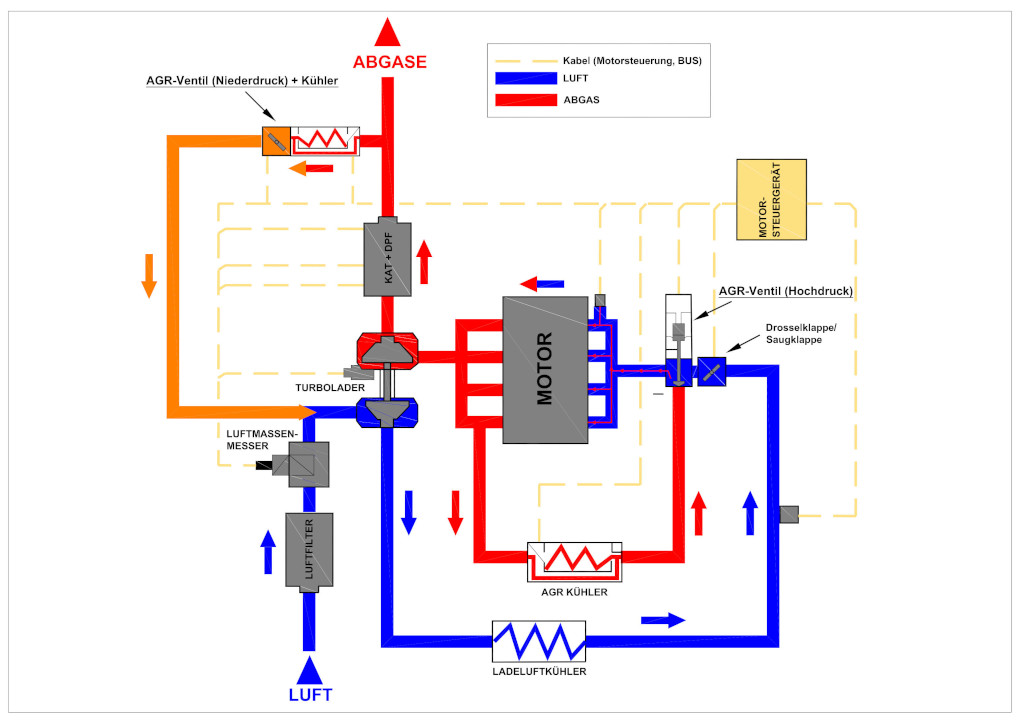
4) Low-pressure EGR valve (LP EGR)
To meet the emission limits starting from the Euro 6 emissions standard, the previous high-pressure exhaust gas recirculation system is no longer sufficient.
An additional low-pressure EGR system, abbreviated ND-EGR, is required.
The low-pressure system is installed in vehicles from approximately 2015 onwards and is located near the catalytic converter.
In this process, the exhaust gas is taken from the low-pressure side behind the particulate filter and reintroduced before the compressor of the turbocharger. The dosage is controlled by the low-pressure EGR valve. An exhaust flap provides the necessary exhaust backpressure. This method continues to reduce nitrogen oxides. The combination of the high-pressure and low-pressure EGR systems achieves nearly a 90% reduction in nitrogen oxides in diesel vehicles. Filters before the exhaust (e.g., catalytic converter, DPF, etc.) also contribute to this.
5) EGR valve for gasoline engines
EGR valves for gasoline engines work fundamentally the same as in diesel engines. The created vacuum draws in the exhaust gases and is regulated by the exhaust gas recirculation valve. However, in gasoline engines, the main objective is to reduce fuel consumption. The three-way catalytic converter, which is only installed in gasoline engines, does most of the work regarding nitrogen oxide reduction. Additionally, carbon buildup or soot formation in the EGR valve is eliminated in gasoline engines, which often causes failure in diesel engines.
The first EGR systems were even first used in petrol vehicles in the 1970s. This technology was only introduced for diesel cars in the 1990s.
6) Check EGR valve function
In principle, the EGR valve can be checked for gasoline and diesel engines using the same procedure:
If the negative pressure generated drops too quickly or the idling does not deteriorate, there is a defect in the exhaust gas recirculation system.
This method only works with pneumatically or electro-pneumatically controlled EGR valves. For purely electric EGR valves in newer vehicles, the most sensible method of testing is with a diagnostic tool. If you don't find a vacuum actuator in the engine bay, you most likely have a purely electric control system.
7) Causes of defective EGR valve
The most common cause in a diesel vehicle is a carbonized and clogged EGR valve due to soot.
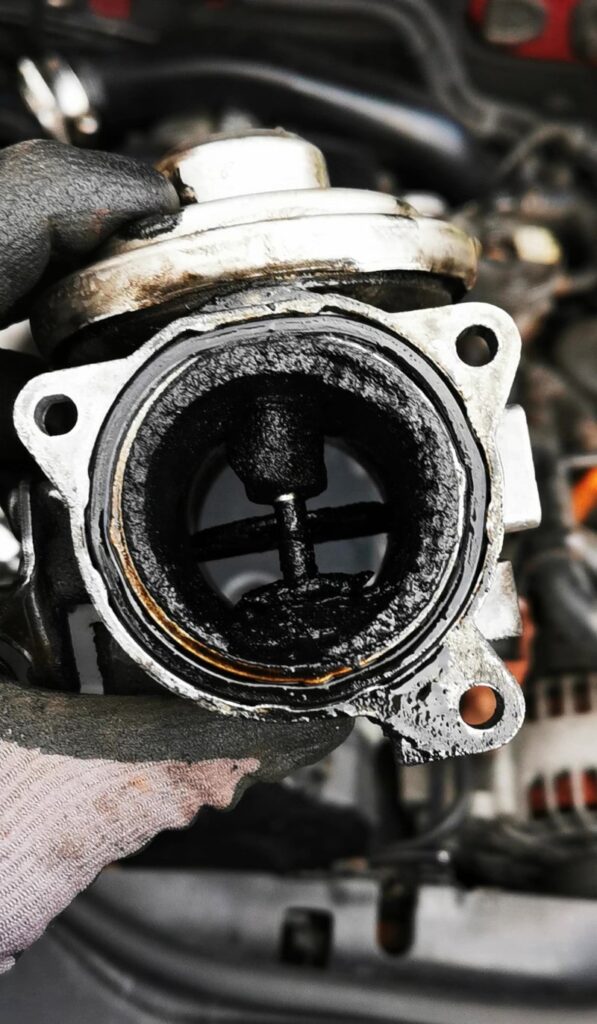

In most cases, it is sufficient to remove and clean the EGR valve.
Other possible causes or diagnoses are
8) The problem of exhaust gas recirculation & partial solution
The exhaust gas recirculation is primarily good for the environment, but bad for the engine technology itself. When exhaust gases are recirculated into the engine compartment, significant carbon buildup occurs in the intake tract of diesel engines. The "soot layer" can even become so thick that the diameter of the pipes, and thus the airflow, is reduced.
Theoretically, you can solve the problem by deactivating the EGR valve (keeping the EGR permanently closed). However, deactivating it is illegal and counterproductive in terms of environmental protection.
Alternatively, with the right driving style and maintenance, you can minimize carbon buildup and preserve the EGR valve.
Regardless, you should occasionally clean the EGR valve. Every 80,000 km is a good interval. This will help prevent carbon buildup and subsequent damage.
* Affiliate links are marked with a *. Nothing changes for you and the offer/price remains the same. You can find more information about affiliate links here.
More Articles
BMW Sport Plus codieren: Fahrmodus freischalten – Anleitung
BMW Sport & Comfort Plus codierenFahrmodus freischalten – Anleitung BMW-Codierung leicht gemacht – In dieser Anleitung erfährst du Schritt für…
BMW Codieren Software Vergleich 2025 | ESys, BimmerCode & Co
BMW Codieren Software VergleichESys, BimmerCode & Co. Um einen BMW zu codieren gibt es mittlerweile unzählige Tools. Unterschiedliche Softwareanbieter bieten…
BMW Emergency Call System Error Battery Replacement | G-Series GUIDE
BMW Notruf Systemfehler?Lösung: Batterie wechseln! Der bekannte BMW Notruf Systemfehler (B7F341) tritt bei vielen BMW Fahrzeugen auf, egal ob E-Serie,…